Bulimia nervosa
Bulimia Nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of binge eating followed by inappropriate compensatory behaviors such as self-induced vomiting, fasting, excessive exercise, and the abuse of laxatives or diuretics. This condition typically involves an intense fear of gaining weight and an obsession with body shape and weight.
Onset
The onset of bulimia nervosa typically occurs during adolescence or young adulthood and affects women more frequently than men. It is estimated that 1-2% of young women will develop bulimia nervosa in their lifetime.
Cause
The exact cause of bulimia nervosa is not known, but it is believed to result from a combination of psychological, genetic, and environmental factors. Psychological factors include low self-esteem, perfectionism, and an excessive concern with weight and body shape. Family and twin studies suggest that there may be a genetic component to the development of bulimia nervosa. Environmental factors include societal pressure to be thin, trauma, and life stress.
Symptoms
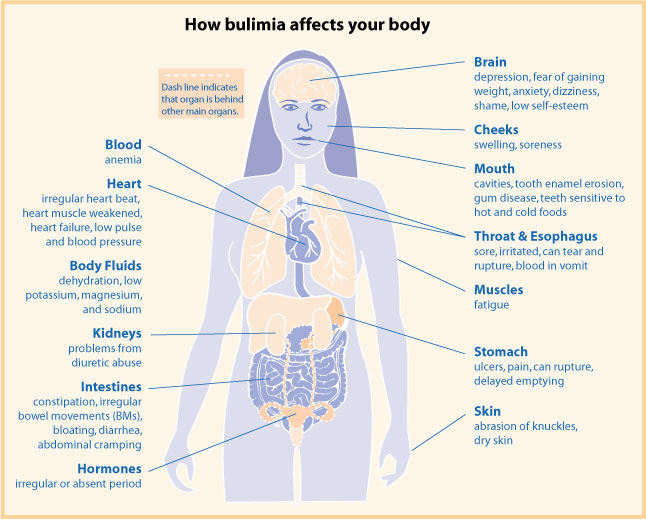
The hallmark symptoms of bulimia nervosa include recurrent episodes of binge eating and purging, extreme concern with body weight and shape, and frequent weight fluctuations. Additionally, individuals with bulimia nervosa may exhibit irregular menstrual cycles, calluses on their knuckles from inducing vomiting, dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and dental problems from exposure to stomach acid during purging.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of bulimia nervosa is made based on criteria specified in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition (DSM-5). These criteria include recurrent binge eating, purging behavior, and a distorted body image or self-esteem that is overly influenced by weight and shape.
Treatment
Treatment for bulimia nervosa typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medications, and nutritional counseling. Psychotherapy approaches that have been found to be effective include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT). Medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can be effective in reducing binge eating and purging behaviors. Nutritional counseling is also an important component of treatment for bulimia nervosa, as individuals with this condition often have a history of disordered eating and malnutrition.
Frequently asked questions
- Are patients with Bulimia underweight, overweight or obese?
- Unlike anorexia nervosa, people with bulimia nervosa usually maintain what is considered a healthy or relatively normal weight.
- What are the symptoms of Bulimia?
Symptoms include:
- Chronically inflamed and sore throat
- Swollen salivary glands in the neck and jaw area
- Worn tooth enamel and increasingly sensitive and decaying teeth as a result of exposure to stomach acid
- Acid reflux disorder and other gastrointestinal problems
- Intestinal distress and irritation from laxative abuse
- Severe dehydration from purging of fluids
- Electrolyte imbalance (too low or too high levels of sodium, calcium, potassium and other minerals) which can lead to stroke or heart attack
- How do you diagnose Bulimia? A dental exam may show signs of cavities or gingivitis (infection of gums). The enamel of the teeth may be worn away or pitted because of too much exposure to the acid in vomit. A physical exam may also show:
Broken blood vessels in the eyes (from the strain of vomiting)
- Dry mouth
- Pouch-like look to the cheeks
- Rashes and pimples
- Small cuts and calluses across the tops of the finger joints from forcing oneself to vomit called Russel's sign
- Blood tests may show an electrolyte imbalance (such as low potassium level) or dehydration.
- How do you treat Bulimia? Treatment depends on how severe the bulimia is, and the person's response to treatments:
- Support groups may be helpful for mild bulimia without other health problems.
- Counseling, such as talk therapy and nutritional therapy are the first treatments for bulimia that does not respond to support groups.
- Medicines that also treat depression, known as selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are often used for bulimia. Combining talk therapy with SSRIs may help, if talk therapy alone does not work.
- What is the prognosis for Bulimia? Bulimia is a long-term illness. Many people will still have some symptoms, even with treatment.
- What are the possible complications of Bulimia? Bulimia can be dangerous. It may lead to serious health problems over time. For example, vomiting over and over can cause:
- Stomach acid in the esophagus (the tube that moves food from the mouth to the stomach). This can lead to permanent damage of this area.
- Tears in the esophagus
- Dental cavities
- Swelling of the throat
- Vomiting and overuse of enemas or laxatives can lead to:
- Dehydration, electrolyte imbalances etc
- Electrolyte imbalance (too low or too high levels of sodium, calcium, potassium and other minerals) which can lead to stroke or heart attack, heart rhythm problems etc.
Also see
How can W8MD help with food addiction?
Pronounced weightMD, our state of the art W8MD physician medical weight loss, sleep, holistic IV nutrition and aesthetic medicine programs can help you not only to lose weight, and sleep better but also look your best!
The Center’s team of practitioners are among the most qualified, dedicated and hospitable professionals in the industry. Since its inception in 2011, W8MD’sinsurance physician weight loss program has successfully helped thousands of patients succeed in not only losing weight but also keep it off with an ongoing maintenance plan.
W8MD’s insurance physician weight loss program is unique in many ways with a comprehensive multidisciplinary approach to weight loss that addresses all the complex issues leading to weight gain, both in adults and children.
References
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5). American Psychiatric Publishing.
- National Eating Disorders Association. (2020). Bulimia Nervosa. https://www.nationaleatingdisorders.org/learn/by-eating-disorder/bulimia
- Smink, F. R., Van Hoeken, D., & Hoek, H. W. (2012). Epidemiology of eating disorders: incidence, prevalence and mortality rates. Current Psychiatry Reports, 14(4), 406-416.
- National Institute of Mental Health. (2021). Eating Disorders. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/eating-disorders/index.shtml
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP1 injections from $50.00^
W8MD Weight Loss, Sleep & Medspa Centers is a network of medical centers located in New York, and Pennsylvania, that provide comprehensive care for weight loss, sleep disorders, and aesthetic treatments. We can obtain insurance prior authorizations when coverage available.
Book appointments
Locations
W8MD location(s):
- NYC weight loss: NYC medical weight loss, sleep and medspa: 2632 E 21st St., Suite L3, Brooklyn, NY 11235 Contact: (718)946-5500
- Philadelphia weight loss - 1718 Welsh Road, 2nd Floor, Ste C, Philadelphia, PA 19115 (215)676-2334
- W8MD's Weight loss diet - Recipes (WikiMD)
- Links: Weight loss | Sleep medicine | Medical spa | Nutrition | Success stories |
- Diet pills: Phentermine, Phen/Topiramate, Wegovy, Saxenda, Zepbound, Mounjaro, Contrave, Diethylpropion etc.
- Resources: W8MD diet | Keto diet guide | Free Ebook | 12 Ways to lose weight quickly | 8 Amazing Weeks
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight, Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
Linkedin_Shiny_Icon ![]()
![]()
![]()
You can now request appointments by text for all existing patients! Simply send your name, date of birth, and preferred date, location & time to Havila at (718) 207-7411.
- ^ Our budget compounded Semaglutide starts from weekly from $50 and up and Tirzepatide from $65.00 and up weekly with insurance. Self pay patients add $50.00 weekly visit fee.
- The prices are for starting dose only and will go up based on the dose. Insurance copays, deductibles and program fees may apply! Individual results may vary.
Also see
This is a short summary article. For quality control, we do not encourage or allow strangers to edit the content.